= S =
Scope note
A scope note may be a definition. It may include : Including concepts, excluding concepts; Reference to other terms, Additional instructions,
Source : http://publish.uwo.ca/~craven/677/thesaur/main07.htm [visited 2010-09-15]
Search strategy results
Sensitive search
For a sensitive search you need to think of all the possible ways an author or an indexer might describe each of your key words in phrases. You might find it useful to check with a medical thesaurus or a list of subject heading such as MESH (Medical Subject Headings).
The more alternative terms you use the more results you will get from the search.
Source : NHS FIFE LIBRARY SERVICES: Guide to Literature Searching. Available from: http://www.nhsfifelibraries.scot.nhs.uk/publications/litsearching.doc
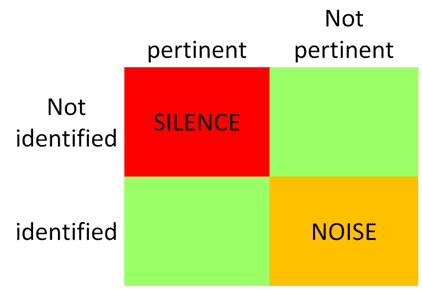
Sensitivity
Sensitivity for a given strategy is defined as the proportion of high quality articles that are retrieved
Source : http://hiru.mcmaster.ca/hiru/HIRU_Hedges_home.aspx
Special queries
Special queries are pre-established queries allowing to identify pertinent references on a specific subject; two kind of special queries are usually available:
- "Evidence based" special queries that are tested against a gold standard (a manual selection of publications that should be retrieved by the electronic search) regarding sensitivity, specificity, precision and accuracy (e.g. Hedges).
- "Experience based" special queries that are not validated against a gold standard
See Appendix 2 for a KCE selection of special queries
Specific search
For a specific search you want to use only terms that relate directly to your question, so you would use only one (or at the most two) way to describe each search term. You may need to check with the MESH as with the databases own thesaurus to ensure that the terms you are using are the terms the indexer would use.
In a specific search, you would apply more Limits. Limits are search terms such as language, age of article, journal title, article type or limits on the populations such as age, gender, ethnic group etc.
You can limit articles NOT to find certain terms, for example you could search for stress but NOT stress fractures.
The more limits you apply to a search the fewer results you will get from that search.
Source : NHS FIFE LIBRARY SERVICES: Guide to Literature Searching. Available from: http://www.nhsfifelibraries.scot.nhs.uk/publications/litsearching.doc
Specificity
specificity is the proportion of low quality or off topic articles not retrieved.
Source : http://hiru.mcmaster.ca/hiru/HIRU_Hedges_home.aspx
SPICE
SPICE is recognises that information practice is a social science, not a “hard science”, by splitting the population component into both setting and perspective. By replacing “outcomes” with “evaluation” the SPICE model incorporates other concepts such as “outputs” and “impact” together with less tangible effects of an intervention
Setting | Where? |
Population | For whom? |
Intervention | What? |
Comparison | Compared with what? |
Evaluation | With what result? |
Source: Booth A. Clear and present questions: formulating questions for evidence based practice. Library Hi Tech. Vol. 24 No. 3, 2006. pp. 355-368
SPIDER
SPIDER is an alternative search strategy tool for qualitative/mixed methods research
Sample |
Phenomenon of Interest |
Design |
Evaluation |
Research type |
Structured question
A structured question put together different elements of the same concept (facet).
Examples : ECLIPSE, PICO, PIRT, SPICE, SPIDER
Sub-headings
See : Qualifiers
Subject heading
Subject heading is a word or phrase from a controlled vocabulary which is used to describe the subject of a document or a class of documents.
Source : http://www.iva.dk/bh/lifeboat_ko/concepts/subject_heading.htm
Subset
PubMed subset is the application of a Special query to PubMed records.
Clinical queries search the user’s keyword in a subset of PubMed instead of the whole PubMed set.
E.g.: Systematic Reviews subset on PubMed (source: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/bsd/pubmed_subsets/sysreviews_strategy.html)