APPENDIX 4: SEARCH ELECTRONIC DATABASES GLOSSARY

= A =
Accuracy
Accuracy is the proportion of all articles that are correctly categorized by the search strategy
Source : http://hiru.mcmaster.ca/hiru/HIRU_Hedges_home.aspx
Adjacent
physician adj5 relationship retrieves records that contain the words physician and relationship within five words of each other in either direction.
E.g. physician patient relationship, patient physician relationship, relationship of the physician to the patient, and so on.
Source: OVID help, available from: http://www.ovid.com /site/help/documentation/ospb/en/syntax.htm#operators
AND
 The AND operator lets you retrieve only those records that include all of your search terms. For example, the search “blood pressure AND stroke” retrieves only those records that contain both terms “blood pressure” and “stroke” together in the same record. Results exclude records that do not contain both terms.
The AND operator lets you retrieve only those records that include all of your search terms. For example, the search “blood pressure AND stroke” retrieves only those records that contain both terms “blood pressure” and “stroke” together in the same record. Results exclude records that do not contain both terms.
Source : OVID help. Available form: http://www.ovid.com/site/help/documentation/ospb/en/syntax.htm#operators
Image source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:LogicGates.svg
Approach
- Identify your problem
- Define a structured question
- Find the best evidence
- How valid is the study?
- What are the results?
- How should I apply the results to patient care?
Source: Guyatt G, Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group. Users' guides to the medical literature : a manual for evidence-based clinical practice. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2008.

= B =
Bibliographic indexes
A bibliographic index is an "open-end finding guide to the literature of an academic field or discipline (example: Philosopher's Index), to works of a specific literary form (Biography Index) or published in a specific format (Newspaper Abstracts), or to the analyzed contents of a serial publication (New York Times Index). Indexes of this kind are usually issued in monthly or quarterly paperback supplements, cumulated annually.
Some bibliographic indexes are also published online, in which case they are called bibliographic databases
Source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bibliographic_index [visited 2010-09-15]
Bibliographical databases
A bibliographic database is a database of bibliographic records, an organized digital collection of references to published literature, including journal and newspaper articles, conference proceedings, reports, government and legal publications, patents, books, etc. In contrast to library catalogue entries, a large proportion of the bibliographic records in bibliographic databases describe analytics (articles, conference papers, etc.) rather than complete monographs, and they generally contain very rich subject descriptions in the form of keywords, subject classification terms, or abstracts.
A bibliographic database may be general in scope or cover a specific academic discipline. A significant number of bibliographic databases are still proprietary, available by licensing agreement from vendors, or directly from the abstracting and indexing services that create them.
Many bibliographic databases evolve into digital libraries, providing the full-text of the indexed contents. Others converge with non-bibliographic scholarly databases to create more complete disciplinary search engine systems, such as Chemical Abstracts or Entrez
Source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bibliographic_database [visited 2010-09-15]
Booleans operators
See : ADJACENT, AND, NEAR, NOT, OR
Broader term
In the hierachy of a thesaurus, relationship between a term and a more generic term.

= C =
Context
Thesauri are multi-hiérarchical: one Heading can be found at several places; each place in the hierarchy of the thesaurus is called a context.
Clinical queries
See: Special queries, Subset

= D =
Descriptor
See : Subject Heading.

= E =
ECLIPSE
ECLIPSE is useful for management, service or health policy related issues.
Expectations : | This is the improvement or innovation or information that you want to see. |
Client group : |
|
Location : |
|
Impact : | What is the change in the service which is being looked for? What would constitute success? How is this being measured? |
Professionals Involved : |
|
Service : | For which service are you looking for information? |
Evaluation : |
|
Source : NHS FIFE LIBRARY SERVICES: Guide to Literature Searching. Available from: http://www.nhsfifelibraries.scot.nhs.uk/publications/litsearching.doc [visited 2010-09-15]
Evidence pyramid
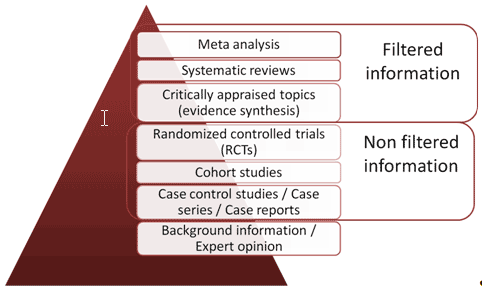
Based on: http://smlweb.aub.edu.lb/Tutorial.aspx?file=Tutorials/principles.html and http://nyu.libguides.com/content.php?pid=27011&sid=234199#systematic [visited 2010-09-15]
Evidence source type
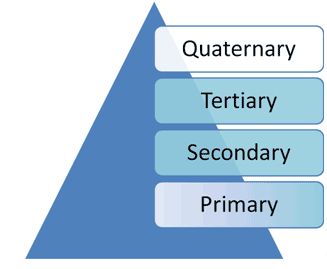
- Quaternary : Clinical guidelines/ consensus meetings/standards
- Tertiary : Systematic reviews/meta-analyses/EBM publications
- Secondary : Bibliographical databases
- Primary : Journals, reports
Source : CEBAM
Explosion (Explode)
Explosion consists of selecting one term in the hierarchy of a thesaurus, and including all narrower terms.

= F =
Focus
Focus consists of selecting a Heading as Major topic. It reduces the amount of results while keeping a good pertinence.

= H =
Hedges
Hedges are special queries developped by HIRU center of the McMaster University (Canada).
See : Special queries

= I =
Institutional repositories
While the main purposes of institutional repositories are to bring together and preserve the intellectual output of a laboratory, department, university, or other entity, the incentives and commitments to change the process of scholarly communication have also begun serving as strong motivators.
Source : http://www.infotoday.com/searcher/may04/drake.shtml [visited 2010-09-15]

= J =
Journal’s impact factor
A journal’s impact factor is based on two elements: the numerator, which is the number of cites in the current year to any items published in the journal in the previous 2 years; and the denominator, the number of substantive articles (source items) published in the same 2 years.
Source: Eugene Garfield. The Agony and the Ecstasy—The History and Meaning of the Journal Impact Factor. International Congress on Peer Review And Biomedical Publication Chicago, September 16, 2005

= M =
Major topics (Medline / MeSH)
Asterisks on MeSH headings and subheadings (e.g., Wound Healing/radiation effects*) designate that they are the major topics of the article, usually obtained from the title and/or statement of purpose
Non-major (non-asterisked) headings and subheadings are usually additional topics substantively discussed within the article, terms added to qualify a major topic (…).
The only indexed MEDLINE citations without an asterisked heading are some biographies in which the subject’s name may be considered the only major point. (…)
Source : http://www.nlm.nih.gov/bsd/disted/mesh/major.html
Mapping
In resources with controlled vocabulary, you can map search terms to subject headings
Source: OVID help. Available form http://www.ovid.com/site/help/documentation/ospb/en/advanced.htm#map

= N =
Narrower term (NT)
In the hierarchy of a thesaurus, relationship between a term and a more specific term
NEAR
Physician NEAR relationship retrieves records that contain the words in the same field
E.g. both words in the Title; in the abstract, and so on
Source : OVID help. Available form: http://www.ovid.com/site/help/documentation/ospb/en/syntax.htm#operators
NOT
 The NOT operator lets you retrieve records that contain your first term but exclude the second term. In this way, you can restrict the scope of your results. For example, the search health reform not health maintenance organizations retrieves only those records that contain the term health reform but exclude the term health maintenance organizations.
The NOT operator lets you retrieve records that contain your first term but exclude the second term. In this way, you can restrict the scope of your results. For example, the search health reform not health maintenance organizations retrieves only those records that contain the term health reform but exclude the term health maintenance organizations.
Source : OVID help. Available form: http://www.ovid.com/site/help/documentation/ospb/en/syntax.htm#operators
Image source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:LogicGates.svg [visited 2010-09-15]

= O =
OAI repositories
See : Institutional repositories
Open Access (OA)
By 'open access' to this literature, we mean its free availability on the public internet, permitting any users to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of these articles, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without financial, legal, or technical barriers other than those inseparable from gaining access to the internet itself. The only constraint on reproduction and distribution, and the only role for copyright in this domain, should be to give authors control over the integrity of their work and the right to be properly acknowledged and cited.
Source: http://www.earlham.edu/~peters/fos/boaifaq.htm#openaccess
Open archives initiative (OAI)
The Open Archives Initiative develops and promotes interoperability standards that aim to facilitate the efficient dissemination of content. OAI has its roots in the open access and institutional repository movements. Continued support of this work remains a cornerstone of the Open Archives program. Over time, however, the work of OAI has expanded to promote broad access to digital resources for eScholarship, eLearning, and eScience.
Source : http://www.openarchives.org/
Operators (Booleans)
See : ADJACENT, AND, NEAR, NOT, OR
OR
![]() The OR operator lets you retrieve records that contain any of your search terms. For example, the search “heart attack OR myocardial infarction” retrieves records that contain “heart attack”, “myocardial infarction” or both terms. Results are all inclusive
The OR operator lets you retrieve records that contain any of your search terms. For example, the search “heart attack OR myocardial infarction” retrieves records that contain “heart attack”, “myocardial infarction” or both terms. Results are all inclusive
Source : OVID help. Available form: http://www.ovid.com/site/help/documentation/ospb/en/syntax.htm#operators
Image source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:LogicGates.svg

= P =
Permuted index
The Permuted index is an alphabetical list of all entry terms of a thesaurus. The entry term sends to the retained term (Subject Heading).
PICO
PICO is useful for medical questions and for topics where one thing is being compared with another.
Patient :. | This is the “Who”. For this you need to think of age, sex, ethnic origins or other defining characteristics of the patient and the population |
Intervention : | This is also sometimes known as exposure, and makes up the “What”. This is what is happening to the patient or population, so it could be a drug or a therapy, a screening questionnaire or a health improvement programme. |
Comparison : | With what is the intervention (or indeed population) being compared? This could be a control group. |
Outcome : | What outcome do you expect to see? For example, you may be interested in knowing whether an intervention has a health benefit, or whether an exposure results in mortality. |
Source : NHS FIFE LIBRARY SERVICES: Guide to Literature Searching. Available from: http://www.nhsfifelibraries.scot.nhs.uk/publications/litsearching.doc
PICO-Timeframe : | This refers to one or more time-related variables such as the length of time the treatment should be prescribed or the point at which the outcome is measured. |
PICOT-T | Type of study design |
| PICO-Context: | |
| PICO-Setting: |
PIRT
Source:
| P | Population |
| I | Index test |
| R | Reference test |
| T | Target disorer |
Precision
Precision is the proportion of retrieved articles that are of high quality

= Q =
Qualifiers
Qualifiers (subheadings) afford a convenient means of grouping together those citations which are concerned with a particular aspect of a subject. Not every qualifier is suitable for use with every subject heading.

= R =
Related terms (see also)
Associative relationship
Relationships
Thesaurus relationships include Broader terms, Narrower terms, Used for, Use, Related terms / See also
Rotated index
See: Permuted index

= S =
Scope note
A scope note may be a definition. It may include : Including concepts, excluding concepts; Reference to other terms, Additional instructions,
Source : http://publish.uwo.ca/~craven/677/thesaur/main07.htm [visited 2010-09-15]
Search strategy results
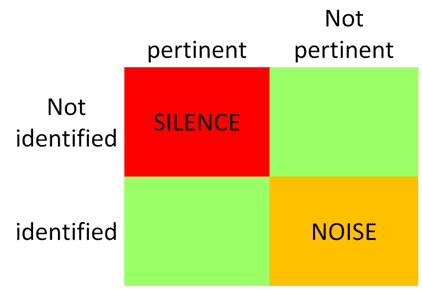
Sensitive search
For a sensitive search you need to think of all the possible ways an author or an indexer might describe each of your key words in phrases. You might find it useful to check with a medical thesaurus or a list of subject heading such as MESH (Medical Subject Headings).
The more alternative terms you use the more results you will get from the search.
Source : NHS FIFE LIBRARY SERVICES: Guide to Literature Searching. Available from: http://www.nhsfifelibraries.scot.nhs.uk/publications/litsearching.doc
Sensitivity
Sensitivity for a given strategy is defined as the proportion of high quality articles that are retrieved
Source : http://hiru.mcmaster.ca/hiru/HIRU_Hedges_home.aspx
Special queries
Special queries are pre-established queries allowing to identify pertinent references on a specific subject; two kind of special queries are usually available:
- "Evidence based" special queries that are tested against a gold standard (a manual selection of publications that should be retrieved by the electronic search) regarding sensitivity, specificity, precision and accuracy (e.g. Hedges).
- "Experience based" special queries that are not validated against a gold standard
See Appendix 2 for a KCE selection of special queries
Specific search
For a specific search you want to use only terms that relate directly to your question, so you would use only one (or at the most two) way to describe each search term. You may need to check with the MESH as with the databases own thesaurus to ensure that the terms you are using are the terms the indexer would use.
In a specific search, you would apply more Limits. Limits are search terms such as language, age of article, journal title, article type or limits on the populations such as age, gender, ethnic group etc.
You can limit articles NOT to find certain terms, for example you could search for stress but NOT stress fractures.
The more limits you apply to a search the fewer results you will get from that search.
Source : NHS FIFE LIBRARY SERVICES: Guide to Literature Searching. Available from: http://www.nhsfifelibraries.scot.nhs.uk/publications/litsearching.doc
Specificity
specificity is the proportion of low quality or off topic articles not retrieved.
Source : http://hiru.mcmaster.ca/hiru/HIRU_Hedges_home.aspx
SPICE
SPICE is recognises that information practice is a social science, not a “hard science”, by splitting the population component into both setting and perspective. By replacing “outcomes” with “evaluation” the SPICE model incorporates other concepts such as “outputs” and “impact” together with less tangible effects of an intervention
Setting | Where? |
Population | For whom? |
Intervention | What? |
Comparison | Compared with what? |
Evaluation | With what result? |
Source: Booth A. Clear and present questions: formulating questions for evidence based practice. Library Hi Tech. Vol. 24 No. 3, 2006. pp. 355-368
SPIDER
SPIDER is an alternative search strategy tool for qualitative/mixed methods research
Sample |
Phenomenon of Interest |
Design |
Evaluation |
Research type |
Structured question
A structured question put together different elements of the same concept (facet).
Examples : ECLIPSE, PICO, PIRT, SPICE, SPIDER
Sub-headings
See : Qualifiers
Subject heading
Subject heading is a word or phrase from a controlled vocabulary which is used to describe the subject of a document or a class of documents.
Source : http://www.iva.dk/bh/lifeboat_ko/concepts/subject_heading.htm
Subset
PubMed subset is the application of a Special query to PubMed records.
Clinical queries search the user’s keyword in a subset of PubMed instead of the whole PubMed set.
E.g.: Systematic Reviews subset on PubMed (source: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/bsd/pubmed_subsets/sysreviews_strategy.html)

= T =
Thesaurus
A thesaurus is a semantic tool used for information retrieval, query expansion and indexing, among other purposes. It is basically a selection of the basic vocabulary in a domain supplemented with information about synonyms, homonyms, generic terms, part/whole terms, “associative terms” and other information (e.g. frequency and history of terms in a given database).
Source : http://www.iva.dk/bh/lifeboat_ko/concepts/thesauri_and_metathesauri.htm
Truncations
Truncated lacking an expected or normal element (as a syllable) at the beginning or end
Source: Meeriam-Webster dictionary. Available from : http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionar
Examples :
Variants | Economical vs Economics | Economic* | 0-n |
Singular vs Plural | Stent vs Stents | Stent? | 0-1 |
EN-us vs EN-uk | Hematology vs Haematology | H?ematology | 0-1 |
Prefixes | Pre natal vs prenatal vs pre-natal | Pre?natal | 0-1 |

= U =
Use
In a thesaurus, relationship between a non-descriptor (entre term) and the descriptor which takes its place
Used for (UF)
In a thesaurus, relationship between the descriptor and the non-descriptor(s) or entry terms it represents